Southern California Edison’s 2026-2028 Wildfire Mitigation Plan: Harnessing Grid Innovations to Enhance Community Safety
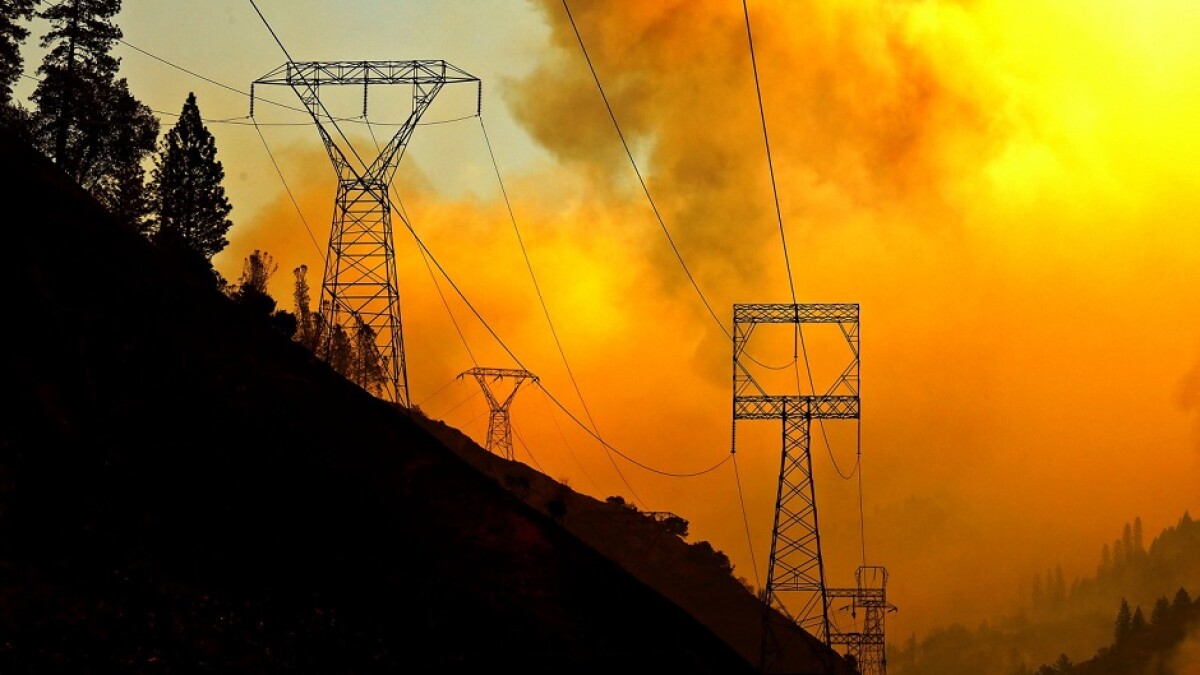
Southern California Edison (SCE), one of the state’s largest electric utilities, has formally submitted its comprehensive Wildfire Mitigation Plan (WMP) for 2026 through 2028 to California’s Office of Energy Infrastructure Safety. This detailed plan builds upon years of ongoing efforts designed to address both immediate and long-term wildfire risks, a critical need given California’s increasing exposure to extreme weather events and the evolving challenges faced by communities across Southern California.
The proposed three-year strategy by SCE underscores a layered defense approach — a multi-faceted, proactive methodology aimed at fortifying the power grid while prioritizing public safety. According to Steven Powell, president and CEO of SCE, “We developed our three-year plan with a layered defense strategy to help safeguard our communities against wildfire threats.” His remarks came in the wake of the devastating wildfires that struck Southern California in January, which painfully highlighted the urgent need for accelerated mitigation efforts and innovative solutions to strengthen grid resilience.
The Growing Wildfire Challenge and the Need for Innovation
Wildfires in California have become more frequent and intense due to a complex interplay of factors such as prolonged droughts, rising temperatures driven by climate change, and changing land-use patterns. These wildfires not only threaten lives and property but also challenge critical infrastructure systems that communities depend on, especially the electric grid.
While it is impossible to eliminate wildfire risk entirely, SCE is determined to reduce that risk as much as technologically and operationally feasible. “The heartbreaking January wildfires in Southern California underscore the importance and urgency in advancing mitigations and using new tools to increase infrastructure resiliency and safety,” Powell emphasized. “While wildfire risk can never be fully eliminated, we continue to harden the grid and invest in innovative approaches to bring us as close to zero as possible.”
Investment and Infrastructure Hardening
To achieve its ambitious goals, SCE plans to invest an estimated $6.2 billion over the next three years. This significant investment will fund a variety of grid modernization and hardening projects, designed to reduce ignition potential and improve response capabilities. Key components of the plan include the installation of at least 440 additional circuit miles of covered conductor — insulated wires designed to reduce wildfire risk by preventing sparks caused by contact with vegetation or other objects. Additionally, SCE aims to install at least 260 circuit miles of underground distribution lines, which are less vulnerable to fire and weather-related damage compared to overhead lines.
Beyond the physical infrastructure upgrades, SCE is also advocating for continued and expanded support of aerial firefighting resources across its service territory. This includes funding for the world’s largest helitankers, equipped with night-time firefighting capabilities. The ability to respond quickly from the air is critical during wildfire events, enabling faster containment and lessening the impact on communities.
Brian Fennessy, fire chief of the Orange County Fire Authority, praised the value of these aerial assets, stating, “With drought conditions across the state, we are preparing for another busy year. The intensity of recent fires is a reminder of how important it is to hit fast and hard — and how devastating it can be if we don’t react quickly. Having dedicated aerial resources funded by SCE allows us to respond swiftly and effectively to wildfires, securing the tools and support needed to protect lives and property.”
Embracing Cutting-Edge Technology for Wildfire Safety

A hallmark of the 2026-2028 WMP is the integration of advanced technology and data-driven methods to improve wildfire mitigation effectiveness. The plan features several innovative tools and systems aimed at enhancing grid safety, reliability, and operational efficiency. These technologies represent the forefront of utility wildfire mitigation practices and signal a shift towards smarter, more adaptive grid management.
- Rapid Earth Fault Current Limiter (REFCL): This device is engineered to immediately detect ground faults — situations where an energized power line comes into contact with the earth — and to quickly reduce voltage on the affected line. Crucially, the REFCL maintains service through the other lines for customers not impacted by the fault. This rapid fault detection and isolation capability minimizes the chance of sparks that could ignite wildfires while maintaining power supply stability.
- Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning: SCE is deploying advanced AI-driven models to enhance the efficiency and accuracy of grid inspections. These tools help prioritize maintenance by analyzing large datasets for signs of equipment degradation or potential failure, thereby enabling faster diagnostics and improved quality control. The use of AI also helps optimize resource allocation and reduce human error in the inspection process.
- Vegetation Management through Remote Sensing: Utilizing LiDAR (Light Detection and Ranging) and satellite imagery, SCE aims to conduct more precise and proactive vegetation monitoring. These technologies allow for detailed mapping of vegetation growth near power lines, enabling targeted trimming and clearance that is both cost-effective and environmentally sensitive. Preventing vegetation-related ignitions remains a cornerstone of wildfire prevention.
- Alternative Undergrounding Techniques: Traditional undergrounding involves trenching the lines deep into the ground, which can be time-consuming and expensive. SCE is exploring alternative approaches that protect lines at ground level, speeding up installation times and reducing costs while still hardening the grid against fire risk.
- Early Fault Detection Expansion: Building on existing grid “health monitoring” systems, the plan includes expanding early fault detection capabilities to 200 new locations. This will enhance SCE’s ability to detect and address equipment failures before they escalate into fire hazards.
Public Safety Power Shutoffs (PSPS) — A Critical, Though Challenging, Tool
Despite ongoing investments in grid hardening, Public Safety Power Shutoffs (PSPS) remain a critical strategy to prevent wildfire ignitions during high-risk weather events, such as extreme winds and dry conditions. PSPS involve proactively de-energizing portions of the electric grid to eliminate potential ignition sources.
Jill C. Anderson, SCE’s executive vice president and chief operating officer, highlighted the lifesaving role of PSPS during the recent January windstorms: “We identified nearly 90 potential ignition sources in the storm’s aftermath that were prevented because the lines were de-energized due to PSPS.” She also noted SCE’s continued investments in protective equipment like covered conductors and fast-acting fuses, which further reduce the risk of fires in high-risk zones.
Recognizing that PSPS events can cause significant inconvenience and hardship for customers, SCE is committed to bolstering customer support and outreach to minimize these impacts. This includes improving communications, offering backup power solutions, and working closely with local communities to ensure preparedness and resilience.
Additional Wildfire Mitigation Measures
Beyond the headline investments and technologies, SCE’s WMP also includes several other enhancements designed to increase transmission resilience and adapt to climate change. These include:
- Transmission Resiliency Improvements: The plan calls for more aggressive structure brushing (clearing vegetation near transmission towers), proactive splice shunting (improving the mechanical and electrical connections on transmission lines), and subtransmission grid hardening projects to reduce vulnerability.
- Undergrounding Expansion: In addition to new underground circuits, the plan explores innovative undergrounding methods tailored to the unique terrain and urban density of Southern California.
- Climate-Integrated Risk Modeling: SCE is incorporating climate change projections and scenarios into its wildfire risk assessment models, helping to anticipate future conditions and better prioritize mitigations.
- AI-Powered Real-Time Fire Assessment: The use of high-definition camera feeds combined with AI analysis allows for continuous monitoring and assessment of fire conditions, improving situational awareness for both utility operators and emergency responders.
- Ongoing Vegetation and Equipment Maintenance: The plan continues foundational mitigation efforts, such as more frequent inspections and vegetation trimming to reduce contact with power lines, which remain essential to wildfire prevention.